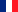
Missing teeth (dental agenesia)
The term agenesia refers to the absence of formation of one or more teeth. It is a phenomenon quite present in the population and not at all rare (2-3% of the population). In general, it affects women more than men, for reasons still unknown. There are several causes, but they can usually be attributed to problems affecting the tooth follicle.
In addition to affecting the functionality of the mouth, agenesia can create psychological discomfort in the relationship with oneself and with others. Some of the teeth most often missing are the lateral incisors of the upper dental arch, which, being visible, creates even more embarrassment. But other dental elements can also be missing such as the second premolars.
At Mercuri Orthodontie, we are specialized in the treatment of dental agenesia, to restore the beauty and health of their smile to patients. So let's see what they are, what causes them and how we deal with them in children and adults.
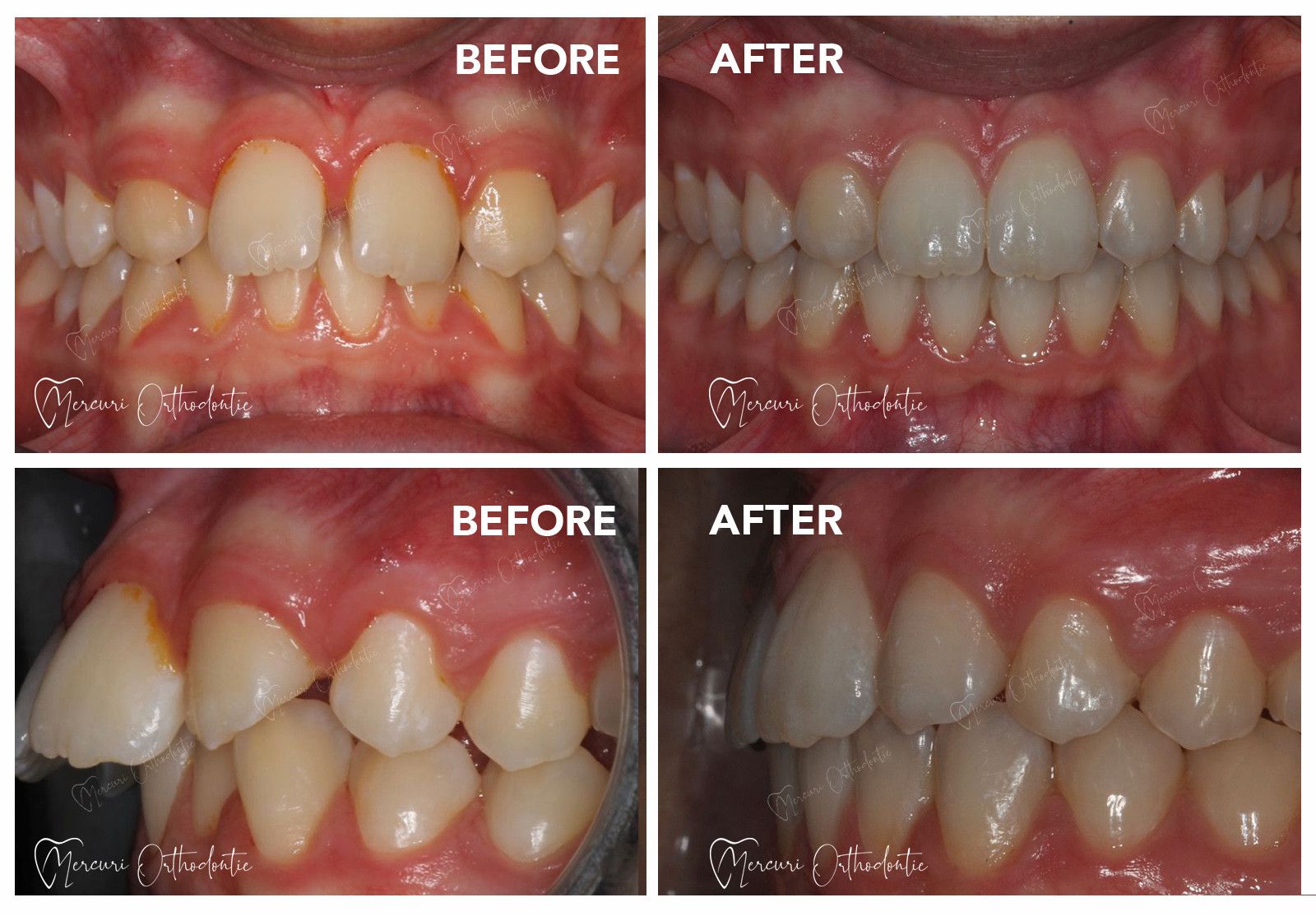
What is dental agenesia
As already mentioned, dental agenesia consists of the absence of certain teeth, milk or permanent. If the deciduous tooth is missing, the corresponding permanent will therefore be missing.
Besides affecting the aesthetic appearance of the person, this abnormality can also lead to malocclusion problems. In fact, neighboring teeth can shift or become crooked. For these reasons, it is essential to intervene as soon as possible, in order to avoid more invasive solutions such as surgery and implantology. Over time, the situation can only escalate, so our advice is to make an orthodontic visit as soon as possible.
A similar problem should not be underestimated at all, due to the serious consequences it can entail. Certain cases of dental agencies fall under the cases taken up by the invalidity insurance (AI).
Causes of dental agenesia
There are several causes for dental agenesia, but are mainly due to genetic and hereditary factors. For example, it is not uncommon to find several people with this problem in the same family.
Treatment of agenesia strictly depends on the age of the patient. In the case of children, it may not be necessary to intervene, as they are baby teeth. Usually in young patients, agenesia is diagnosed around the age of 6 or10, when baby teeth do not fall out because they are not stimulated by perms. Or they fall but never grow back. For these reasons, we recommend that parents visit their children at least around the age of 3 to get an overview of the dental arch and to identify early on the presence of developmental disorders and other issues.
How we treat dental agenesia
Before preparing a therapeutic path, we check the general situation with a panoramic x-ray. An x-ray is needed to check jaw thickness and bone structure. In this way, we can determine whether it is a case of dental agenesia or bone inclusion. The latter is a pathology due to which the teeth have no space to come out and remain embedded in the jaw bone.
We can also understand if there is also a dental overcrowding, in case of partial agenesia, to establish a curative course at 360 degrees.
A possible therapeutic alternative is represented by an orthodontic treatment which makes it possible to achieve a closure of the spaces of agenesia.
Another method is represented by implant surgery, a conservative remedy that involves inserting a titanium screw into the empty space left by the missing tooth. In the next step, fixed artificial prostheses are applied. We opt for this solution by evaluating the patient's age, the agenesia’s typology, the situation of the gums, etc.
There is no better choice than another as the therapy must be individualized on a case-by-case basis depending on the patient's age, bone type and skeletal type.
Speaking of age, patients with agenesia cannot undergo implant surgery until growth has stopped which for women is around 18 and for men between 20 or 21. In the case of pediatric patients in whom it will be decided to prosthetically replace the missing tooth, we will therefore try to keep the deciduous tooth as long as possible, if for example the missing tooth is a premolar. Space must be preserved to perform implant placement as early as possible, but in any case at the end of growth.
If the missing tooth is an incisor, an implant supported crown can be installed later, while maintaining the space with a temporary bridge in the meantime. As we can be able to see, therefore, if the agenesia concerns pediatric patients, the monitoring action over time by the specialist is of fundamental importance. Adequate care will lead to a better health future.
Only then, by making a specific visit to the dentist, is it possible to establish the presence of a dental agenesia problem and to study the best solutions for your case.